Dortmund, 19th July 2022
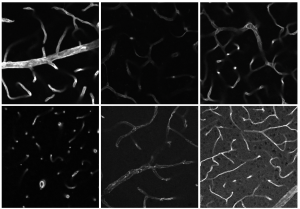
Dr Alexander Knodel completed his doctorate in Physics in only two and a half years. According to the federal record on young scientists (Bundesbericht Wissenschaftlicher Nachwuchs) 2021, he was not only about two years faster than the average PhD student in the natural sciences, but at the age of 27, Knodel was exceptionally young.
At first, however, Knodel did not know whether a degree and later doctorate were the right career path. In the new podcast episode (available only in German), the son of a non-academic family opens up about what ultimately helped him make a choice for his studies and during his time as a PhD student at ISAS. Knodel also talks about his passion for his field of studies and explains, what it has in common with an efficient oven for cancer research.

Dr Alexander Knodel talks to Cheyenne Peters from the Communications team about his fast career path.
© ISAS